Characteristics, techniques, benefits and drawbacks of Fidelity Types
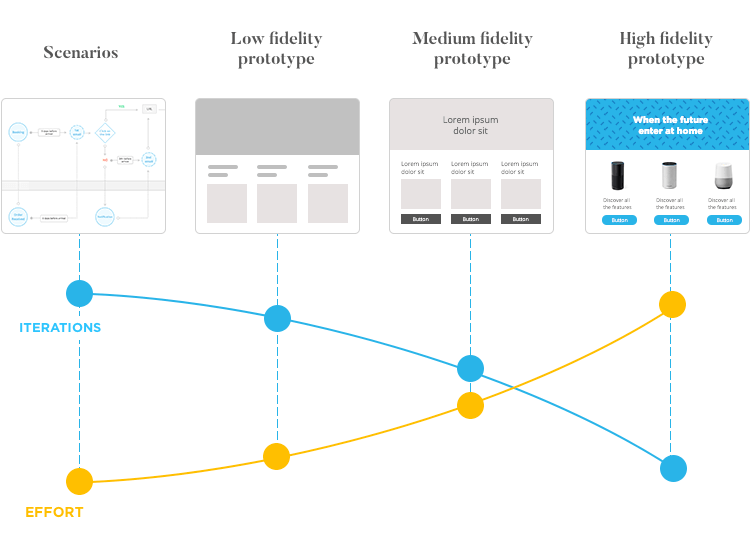
Low-fidelity prototyping is a type of prototyping that involves creating simple, low-detail representations of a product or system. These prototypes are often created using paper or other low-cost materials and are typically used in the early stages of the design process to explore ideas and test basic functionality. Here are some characteristics, techniques, benefits, and drawbacks of low-fidelity prototyping:
Characteristics:
- Low-fidelity prototypes are simple and easy to create.
- They are often created quickly, allowing for rapid iteration and exploration of design ideas.
- They are typically low-detail, meaning that they do not include all of the features and functionality of the final product or system.
- They are often created using low-cost materials, such as paper or cardboard.
Techniques:
- Sketching: Drawing out ideas and designs on paper, whiteboards, or other surfaces.
- Paper prototyping: Creating paper-based representations of a product or system, often using templates or stencils.
- Mockups: Creating physical models of a product or system using cardboard or other low-cost materials.
- Wireframing: Creating basic digital representations of a product or system using simple software tools.
Benefits:
- Low-fidelity prototypes allow for rapid iteration and exploration of design ideas.
- They are cost-effective and easy to create, allowing for more experimentation and testing in the early stages of the design process.
- They can be used to gather feedback from stakeholders and potential users, helping to refine the design and identify potential issues early on.
- They can help to identify usability issues and other problems before a significant investment is made in developing the final product or system.
Drawbacks:
- Low-fidelity prototypes may not provide a realistic representation of the final product or system, which can lead to inaccurate feedback and testing results.
- They may not be suitable for testing more complex functionality or interactions.
- They may require additional effort to create more detailed and accurate representations, which can slow down the design process.
- They may not be suitable for all types of products or systems, depending on the level of detail and functionality required.
Mid-fidelity prototyping is a type of prototyping that falls somewhere between low-fidelity prototyping (simple, low-detail representations of a product or system) and high-fidelity prototyping (more realistic, detailed representations of a product or system). Mid-fidelity prototypes are typically created using digital tools and may include more detailed design elements and basic interactivity. Here are some characteristics, techniques, benefits, and drawbacks of mid-fidelity prototyping:
Characteristics:
- Mid-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and interactive than low-fidelity prototypes, but less detailed and interactive than high-fidelity prototypes.
- They are often created using digital tools, such as design software or prototyping tools.
- They may include more detailed design elements, such as colors, typography, and imagery, and basic interactivity, such as clickable buttons and links.
- They are typically used in the middle stages of the design process to refine ideas and test functionality.
- Digital wireframing: Creating basic digital representations of a product or system using simple software tools.
- Interactive prototypes: Creating digital prototypes with basic interactivity, such as clickable buttons and links, using prototyping software or tools.
- Mockups: Creating more detailed physical or digital models of a product or system using more advanced tools and techniques.
Benefits:
- Mid-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and realistic than low-fidelity prototypes, allowing for more accurate feedback and testing results.
- They are more cost-effective and faster to create than high-fidelity prototypes, allowing for more experimentation and testing in the middle stages of the design process.
- They can be used to test basic functionality and interactivity, helping to refine the design and identify potential issues before investing in more advanced development.
- They can be easily shared and tested with stakeholders and potential users, allowing for more widespread feedback and testing.
- Mid-fidelity prototypes may not provide a completely realistic representation of the final product or system, which can lead to inaccurate feedback and testing results.
- They may require additional effort to create more detailed and accurate representations, which can slow down the design process.
- They may not be suitable for testing more complex functionality or interactions, requiring the use of higher-fidelity prototyping techniques.
- They may not be suitable for all types of products or systems, depending on the level of detail and functionality required.
High-fidelity prototyping is a type of prototyping that aims to create a highly realistic representation of a product or system. These prototypes are often created using advanced digital tools and techniques and may include detailed design elements, advanced interactivity, and realistic animations and transitions. Here are some characteristics, techniques, benefits, and drawbacks of high-fidelity prototyping:
Characteristics:
- High-fidelity prototypes are highly detailed and realistic, often resembling the final product or system.
- They are often created using advanced digital tools and techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) software, 3D modeling software, or advanced prototyping tools.
- They may include detailed design elements, such as colors, typography, imagery, and realistic textures and materials.
- They may include advanced interactivity, such as complex animations, transitions, and interactions.
Techniques:
- Computer-aided design (CAD): Creating digital models of products or systems using advanced software tools.
- 3D modeling: Creating detailed 3D models of products or systems using specialized software tools.
- Advanced prototyping tools: Using specialized prototyping tools or software to create highly realistic and interactive prototypes.
Benefits:
- High-fidelity prototypes provide a highly realistic representation of the final product or system, allowing for accurate testing and feedback.
- They are ideal for testing advanced functionality and interactions, such as complex animations and transitions.
- They can be used to simulate real-world scenarios, helping to identify potential issues and opportunities for improvement.
- They can be highly effective in communicating the design vision to stakeholders and potential users, helping to build buy-in and support for the project.
Drawbacks:
- High-fidelity prototypes can be expensive and time-consuming to create, requiring advanced tools and techniques.
- They may not be necessary or practical for all types of products or systems, depending on the level of detail and functionality required.
- They may be too advanced or detailed for some stages of the design process, requiring the use of lower-fidelity prototyping techniques earlier on.
- They may require specialized skills or expertise to create, limiting the ability to create and test prototypes in-house.
Comments
Post a Comment